ChemicalFormulas - Below are any Vocabbulary in test method for distillation of petroleum product (ASTM D86) :
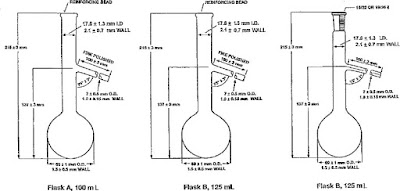
1. Charge volume
n The volume of the specimen, 100 mL, charged to the distillation flask at the temperature specified.
2. Decomposition
n of a hydrocarbon, the pyrolysis or cracking of a molecule yielding smaller molecules with lower boiling points than the original molecule. Characteristic indications of thermal decomposition are evolution of fumes and erratic temperature readings that usually decrease after any attempt is made to adjust the heat.
3. Decomposition point
The corrected thermometer reading that coincides with the first indications of thermal decomposition of the liquid in the flask. The decomposition point, as deter- mined under the conditions of this test method, does not necessarily correspond to the decomposition temperature in other applications.
4. Dry point
n the corrected thermometer reading that is observed at the instant the last drop of liquid (exclusive of any drops or film of liquid on the side of the flask or on the temperature sensor), evaporates from the lowest point in the distillation flask.
The end point (final boiling point), rather than the dry point, is intended for general use. The dry point can be reported in connection with special purpose naphthas, such as those used in the paint industry. Also, it is substituted for the end point (final boiling point) whenever the sample is of such a nature that the precision of the end point (final boiling point) cannot consistently meet the requirements given in the precision section.
5. Dynamic holdup
n the amount of material present in the neck of the flask, in the sidearm of the flask, and in the condenser tube during the distillation.
6. Emergent stem effect
n the offset in temperature reading caused by the use of total immersion mercury-in-glass thermometers in the partial immersion mode. In the partial immersion mode, a portion of the mercury thread, that is, the emergent portion, is at a lower temperature than the immersed portion, resulting in a shrinkage of the mercury thread and a lower temperature reading.
7. End point (EP) or final boiling point (FBP)
n the maximum corrected thermometer reading obtained during the test. This usually occurs after the evaporation of all liquid from the bottom of the flask. The term maximum temperature is a frequently used synonym.
8. Front end loss
n loss due to evaporation during transfer from receiving cylinder to distillation flask, vapor loss during the distillation, and uncondensed vapor in the flask at the end of the distillation.
9. Initial boiling point (IBP)
n the corrected thermometer reading that is observed at the instant the first drop of condensate falls from the lower end of the condenser tube.
10. Percent evaporated
n the sum of the percent recovered and the percent loss.
11. Percent loss (or observed loss) in distillation of petroleum product
n one hundred minus the percent total recovery.
12. Corrected loss
n percent loss corrected for barometric pressure.
13. Percent recovered
n the volume of condensate observed in the receiving cylinder, expressed as a percentage of the charge volume, associated with a simultaneous temperature reading.
14. Percent recovery
n the maximum percent recovered, as observed in accordance with 13.
15. Corrected percent recovery
n the percent recovery, adjusted for the difference between the observed loss and the corrected loss, as described in Eq 14.
16. Percent total recovery
n the combined percent recovery and residue in the flask, as determined in accordance with 14.
17. Percent residue
n the volume of residue in the flask, measured in accordance with 1, and expressed as a percentage of the charge volume.
18. Rate of change (or slope)
n the change in temperature reading per percent evaporated or recovered, as described in 10.
19. Temperature lag
n the offset between the temperature reading obtained by a temperature sensing device and the true temperature at that time.
20. Temperature reading
n the temperature obtained by a temperature measuring device or system that is equal to the thermometer reading described in 20.
21. Corrected temperature reading
n the temperature reading, as described in 20, corrected for barometric pressure.
22. Thermometer reading (or thermometer result)
n the temperature of the saturated vapor measured in the neck of the flask below the vapor tube, as determined by the prescribed thermometer under the conditions of the test.
23. Corrected thermometer reading
n the thermometer reading, as described in 22, corrected for barometric pressure.
1. Charge volume
n The volume of the specimen, 100 mL, charged to the distillation flask at the temperature specified.
2. Decomposition
n of a hydrocarbon, the pyrolysis or cracking of a molecule yielding smaller molecules with lower boiling points than the original molecule. Characteristic indications of thermal decomposition are evolution of fumes and erratic temperature readings that usually decrease after any attempt is made to adjust the heat.
3. Decomposition point
The corrected thermometer reading that coincides with the first indications of thermal decomposition of the liquid in the flask. The decomposition point, as deter- mined under the conditions of this test method, does not necessarily correspond to the decomposition temperature in other applications.
4. Dry point
n the corrected thermometer reading that is observed at the instant the last drop of liquid (exclusive of any drops or film of liquid on the side of the flask or on the temperature sensor), evaporates from the lowest point in the distillation flask.
The end point (final boiling point), rather than the dry point, is intended for general use. The dry point can be reported in connection with special purpose naphthas, such as those used in the paint industry. Also, it is substituted for the end point (final boiling point) whenever the sample is of such a nature that the precision of the end point (final boiling point) cannot consistently meet the requirements given in the precision section.
5. Dynamic holdup
n the amount of material present in the neck of the flask, in the sidearm of the flask, and in the condenser tube during the distillation.
6. Emergent stem effect
n the offset in temperature reading caused by the use of total immersion mercury-in-glass thermometers in the partial immersion mode. In the partial immersion mode, a portion of the mercury thread, that is, the emergent portion, is at a lower temperature than the immersed portion, resulting in a shrinkage of the mercury thread and a lower temperature reading.
7. End point (EP) or final boiling point (FBP)
n the maximum corrected thermometer reading obtained during the test. This usually occurs after the evaporation of all liquid from the bottom of the flask. The term maximum temperature is a frequently used synonym.
8. Front end loss
n loss due to evaporation during transfer from receiving cylinder to distillation flask, vapor loss during the distillation, and uncondensed vapor in the flask at the end of the distillation.
9. Initial boiling point (IBP)
n the corrected thermometer reading that is observed at the instant the first drop of condensate falls from the lower end of the condenser tube.
10. Percent evaporated
n the sum of the percent recovered and the percent loss.
11. Percent loss (or observed loss) in distillation of petroleum product
n one hundred minus the percent total recovery.
12. Corrected loss
n percent loss corrected for barometric pressure.
13. Percent recovered
n the volume of condensate observed in the receiving cylinder, expressed as a percentage of the charge volume, associated with a simultaneous temperature reading.
14. Percent recovery
n the maximum percent recovered, as observed in accordance with 13.
15. Corrected percent recovery
n the percent recovery, adjusted for the difference between the observed loss and the corrected loss, as described in Eq 14.
16. Percent total recovery
n the combined percent recovery and residue in the flask, as determined in accordance with 14.
17. Percent residue
n the volume of residue in the flask, measured in accordance with 1, and expressed as a percentage of the charge volume.
18. Rate of change (or slope)
n the change in temperature reading per percent evaporated or recovered, as described in 10.
19. Temperature lag
n the offset between the temperature reading obtained by a temperature sensing device and the true temperature at that time.
20. Temperature reading
n the temperature obtained by a temperature measuring device or system that is equal to the thermometer reading described in 20.
21. Corrected temperature reading
n the temperature reading, as described in 20, corrected for barometric pressure.
22. Thermometer reading (or thermometer result)
n the temperature of the saturated vapor measured in the neck of the flask below the vapor tube, as determined by the prescribed thermometer under the conditions of the test.
23. Corrected thermometer reading
n the thermometer reading, as described in 22, corrected for barometric pressure.
Tag :
vacuum distillation,
distillation column,
fractional distillation,
steam distillation,
distilled water,
azeotropic distillation,
distilling,
distilled,
what is distillation,
distillation apparatus,
molecular distillation,
crude oil distillation,
alcohol distillation,
simple distillation,
distillation process,
distillation tower,
distillate,
fractional distillation of crude oil,
how to make distilled water,
filtration,
reactive distillation,
distilation,
membrane distillation,
distill,
what is distilled water,
extractive distillation,
how to distill water,
water distiller,
cryogenic distillation,
distillates,
distillation unit,
petroleum,
oil refinery,
brent oil,
oil prices,
brent oil price,
oil price chart,
brent crude,
brent crude price,
oil companies,
distillation,
oil price today,
oil and gas,
distillation column,
oil futures,
wti oil price,
oil prices today,
crude oil distillation,
oil price graph,
petroleum distillates,
current oil price,
fractional distillation,
vacuum distillation,
oil refineries,
live oil price,
oil price history,
oil refining,
oil price per barrel,
oil prices chart,
crude distillation unit,
steam distillation,
0 comments
Post a Comment