ChemicalFormulas - Toluene is used as a verification
fluid for calibration; it will yield almost no information on how well an
electronic measurement system simulates the temperature lag of a
liquid-in-glass thermometer. The accuracy and the calibration of the electronic
circuitry or computer algorithms, or both, shall be verified by the use of a
standard precision resistance bench. When performing this verification, no
algorithms shall be used to correct the temperature for lag and the emergent
stem effect.
Verification of the calibration
of temperature measuring devices shall be conducted by distilling toluene in
accordance with of this test method for distillation of petroleum at
atmospheric pressure and comparing the 50 % recovered temperature with that
shown in bellow. If the temperature reading is not within the values shown in the
table bellow for the respective apparatus being used, the temperature
measurement system shall be considered defective and shall not be used for the
test.
Reagent grade toluene andhexadecane (cetane), conforming to the specifications of the Committee on
Analytical Reagents of the American Chemical Society, shall be used. However,
other grades may also be used, provided it is first ascertained that the reagent
is of sufficient purity to permit its use without lessening the accuracy of the
determination.
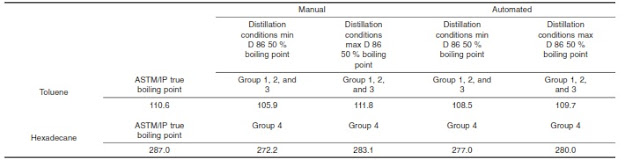
At 101.3 kPa, toluene is shown
in reference manuals as boiling at 110.6°C when measured using a partial
immersion thermometer. Because this test method uses thermometers calibrated
for total immersion, the results typically will be lower and, depending on the
thermometer and the situation, may be different for each thermometer.
At 101.3 kPa, hexadecane is
shown in reference manuals as boiling at 287.0°C when measured using a partial
immersion thermometer. Because of the high melting point of hexadecane, it can be used
to verify the calibration of the temperature measurement system at elevated
temperatures.
0 comments
Post a Comment